List of Common SMT Professional Terminology in Electronics Manufacturing:
List of Common SMT Professional Terminology in Electronics Manufacturing:
-
SMT (Surface Mount Technology): A manufacturing process that involves mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB.
-
PCB (Printed Circuit Board): A board used to support and connect electronic components.
-
DIP (Dual In-line Package): A common packaging form for electronic components.
-
SMD (Surface Mount Device): Electronic components suitable for SMT processes.
-
BGA (Ball Grid Array): A high-density packaging technology.
-
IC (Integrated Circuit): A device that integrates multiple electronic components onto a single chip.
-
PCB Assembly: The process of installing electronic components onto a PCB.
-
Reflow Soldering: A soldering process that melts solder by heating to connect electronic components to a PCB.
-
AOI (Automated Optical Inspection): Used to inspect the quality of electronic components and solder joints on a PCB.
-
X-Ray Inspection: Used to inspect the quality of solder joints inside packages like BGA.
-
ICT (In-Circuit Test): Functional testing of electronic components on a circuit board.
-
FCT (Functional Test): Functional testing of an entire circuit board or product.
-
THT (Through Hole Technology): A process that involves soldering the leads of electronic components through holes in a PCB.
-
SMT Line: An SMT production line that includes equipment such as printers, placement machines, and reflow ovens for SMT processes.
-
Component Mounting: The process of accurately placing SMD components onto a PCB.
-
Stencil Printing: A process that uses a stencil to print solder paste onto a PCB.
-
Pick and Place: The action of a placement machine picking up SMD components from a feeder and placing them onto a PCB.
-
Solder Paste: A mixture of metal powder and flux used for soldering SMD components.
-
Lead-Free Solder: An environmentally friendly solder that does not contain lead.
-
Wave Soldering: A process that applies molten solder to a PCB through a wave to solder through-hole components.
-
Cleaning: The removal of contaminants and flux residues from a circuit board.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that products meet specified quality standards.
-
Yield: The ratio of qualified products to the total production quantity.
-
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge): A phenomenon of electrostatic discharge that can damage electronic components.
-
Reliability: The ability of a product to function normally under specified conditions.
-
PCB Fabrication: The process of manufacturing PCBs, including steps such as design, drilling, and etching.
-
Component Lead Forming: Bending the leads of components into shapes suitable for soldering or installation.
-
Solder Joint: The welded connection point between an electronic component and a PCB.
-
Void: Bubbles or gaps in a solder joint that may affect its quality and reliability.
-
PCB Thickness: The thickness dimension of a PCB board.
-
Copper Thickness: The thickness of the copper foil on a PCB.
-
Impedance Control: Ensuring impedance matching for signal transmission on a PCB.
-
RF PCB: A PCB used for high-frequency signal transmission.
-
Microvia: A via hole with a diameter less than 0.15mm on a PCB.
-
Blind Via: A via hole that connects only internal layers of a PCB.
-
Buried Via: A via hole that is completely embedded within a PCB.
-
PCB Material: Materials commonly used for PCBs include FR-4, Rogers, etc.
-
SMT Component Feeder: A feeder that provides SMD components to a placement machine.
-
Nozzle: The suction nozzle of a placement machine used to pick up and place SMD components.
-
Feeder Calibration: Calibration of the feeder to ensure accurate feeding of SMD components.
-
Component Placement Accuracy: The positional deviation of a component placed by a placement machine.
-
Reflow Profile: The temperature profile inside a reflow oven, indicating the variation of temperature with time, which affects the quality of soldering.
-
Solderability: The ability of an electronic component's lead or PCB pad to be soldered.
-
Flux: A chemical substance used to promote soldering.
-
Solder Spatter: Small particles of solder that are splashed during the soldering process.
-
Tombstoning: A phenomenon where SMD components stand upright after soldering.
-
Component Shift: The deviation of a component's position after placement from its designed position.
-
PCB Warpage: The bending or deformation of a PCB board.
-
SMT Production Line: The entire process of SMT production, including printing, placement, reflow soldering, and other steps.
-
Cycle Time: The time required to complete a production process.
-
SMT Stencil: A template used for printing solder paste.
-
Adhesive: A substance used to secure SMD components in position on the PCB.
-
Component Packaging: The appearance and pin arrangement of an electronic component.
-
QFN (Quad Flat No-Lead): A type of surface-mounted package with no external leads.
-
SOP (Small Outline Package): One of the common integrated circuit packages.
-
SOJ (Small Outline J-lead Package): A small outline package with J-shaped leads.
-
PLCC (Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier): A plastic package with leads for chip carriers.
-
PGA (Pin Grid Array): A package with pins arranged in a grid pattern.
-
COB (Chip-on-Board): A packaging method where the chip is directly mounted on the PCB.
-
Wire Bonding: A technique to connect a chip to a PCB or package substrate using wires.
-
Flip Chip: A technique where the active side of the chip is attached to the PCB or substrate facing down.
-
Underfill: A material used to fill the gap between a chip and the PCB to enhance reliability.
-
PCB Design: The process of designing PCBs, including layout, routing, signal integrity, etc.
-
Gerber File: A graphical file format required for PCB manufacturing.
-
DFM (Design for Manufacturing): A PCB design approach that considers manufacturing processes.
-
NPI (New Product Introduction): The process of introducing a new product into production.
-
BOM (Bill of Materials): A list of raw materials and components required for a product.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The minimum purchase quantity required by a supplier.
-
JIT (Just-in-Time): A production strategy that produces and supplies components based on actual demand.
-
Kanban: A signaling system used to control production processes.
-
Cost of Goods Sold: The direct costs incurred in producing goods for sale.
-
ROI (Return on Investment): A metric used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment.
-
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): A system that integrates enterprise management information.
-
MES (Manufacturing Execution System): Software used to monitor and manage production processes in real-time.
-
Six Sigma: A quality management methodology aimed at reducing defects and improving process stability.

 PCB
PCB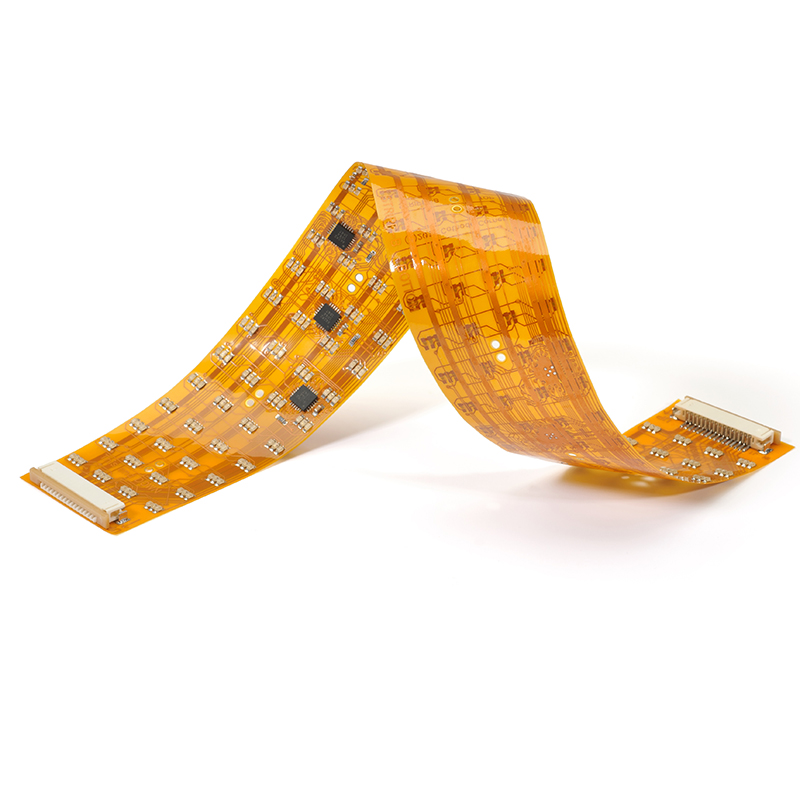 FPC
FPC Rigid-Flex
Rigid-Flex FR-4
FR-4 HDI PCB
HDI PCB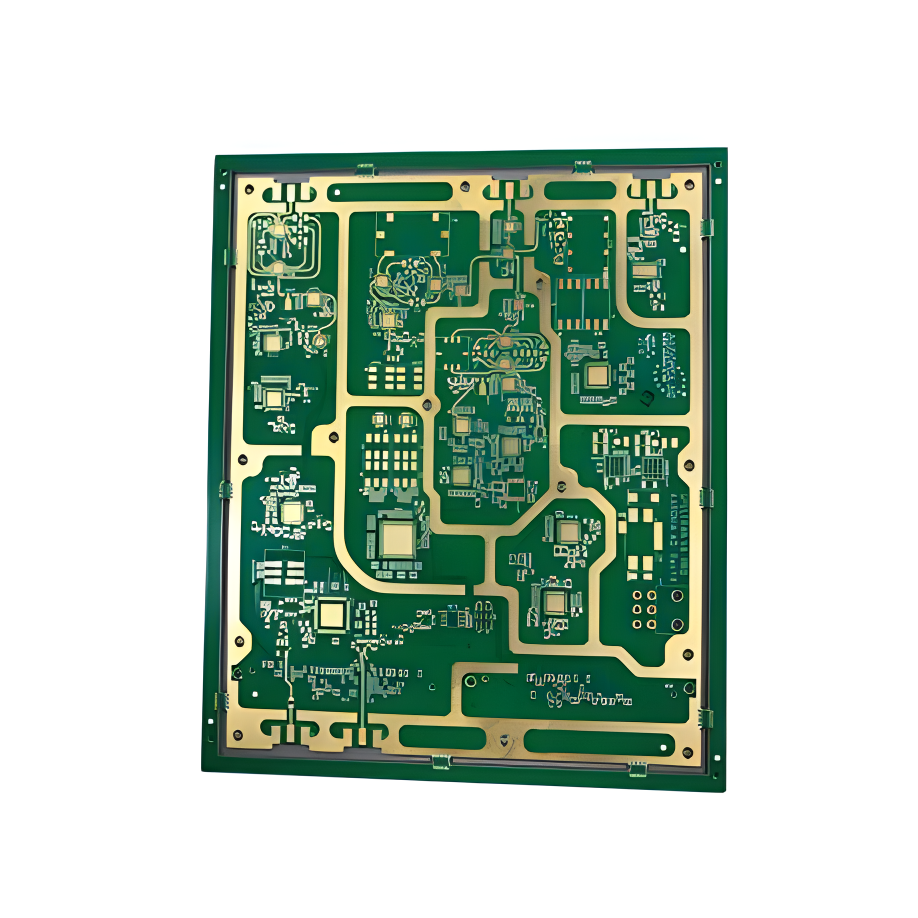 Rogers High-Frequency Board
Rogers High-Frequency Board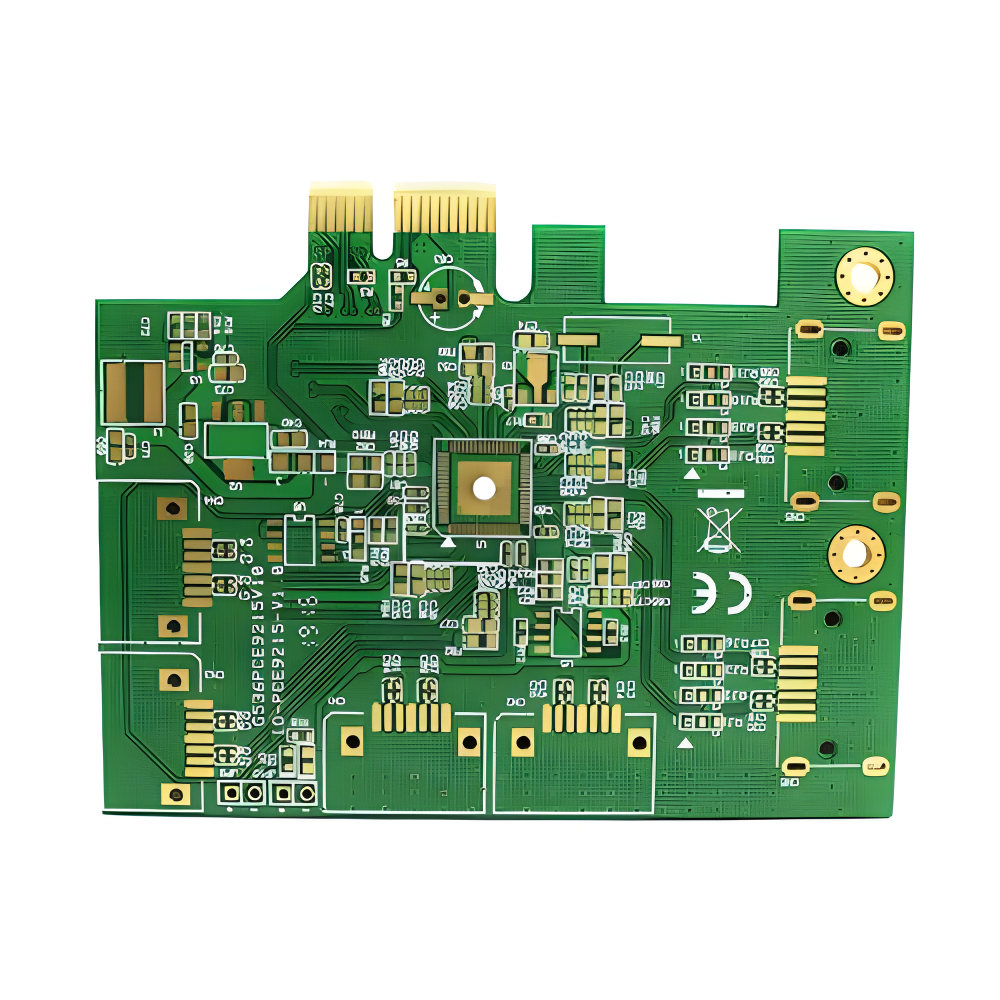 PTFE Teflon High-Frequency Board
PTFE Teflon High-Frequency Board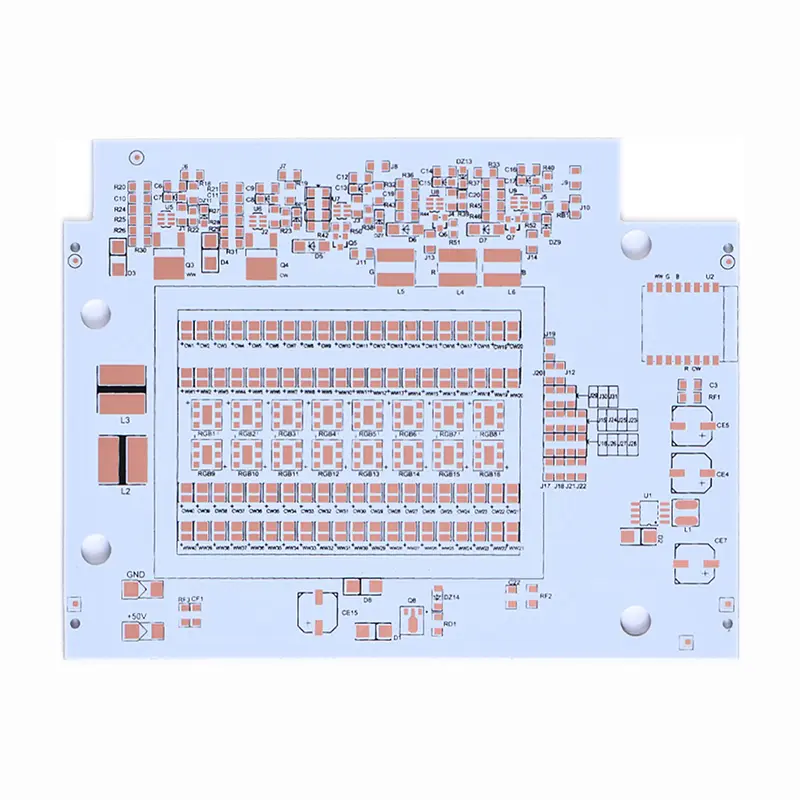 Aluminum
Aluminum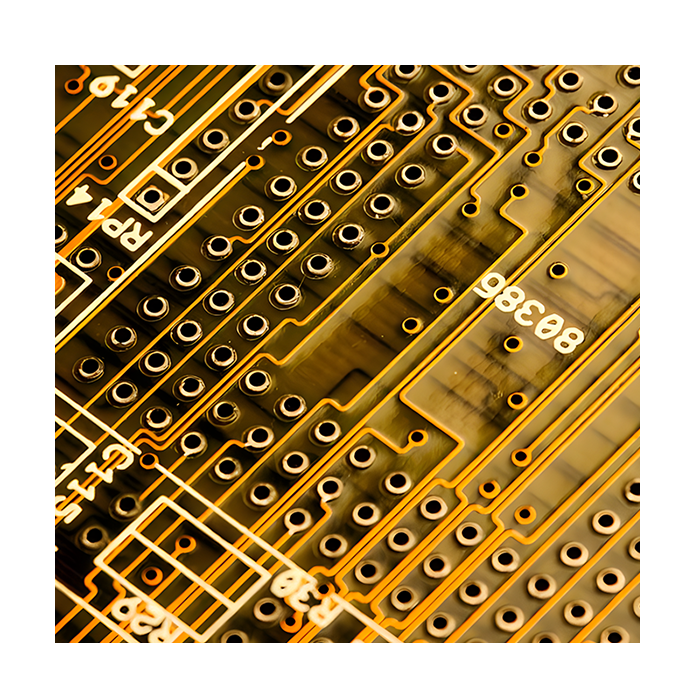 Copper Core
Copper Core PCB Assembly
PCB Assembly LED light PCBA
LED light PCBA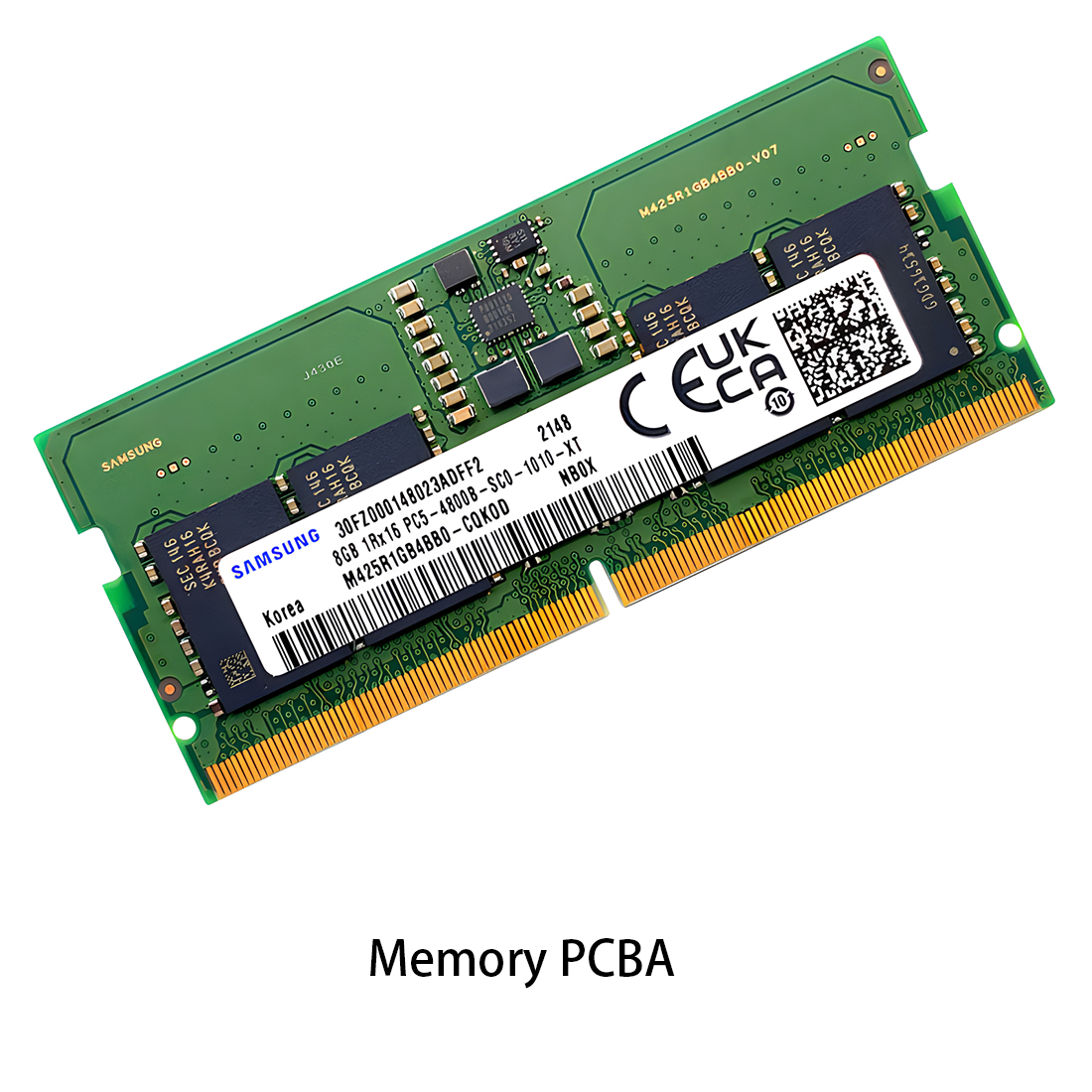 Memory PCBA
Memory PCBA Power Supply PCBA
Power Supply PCBA New Energey PCBA
New Energey PCBA Communication PCBA
Communication PCBA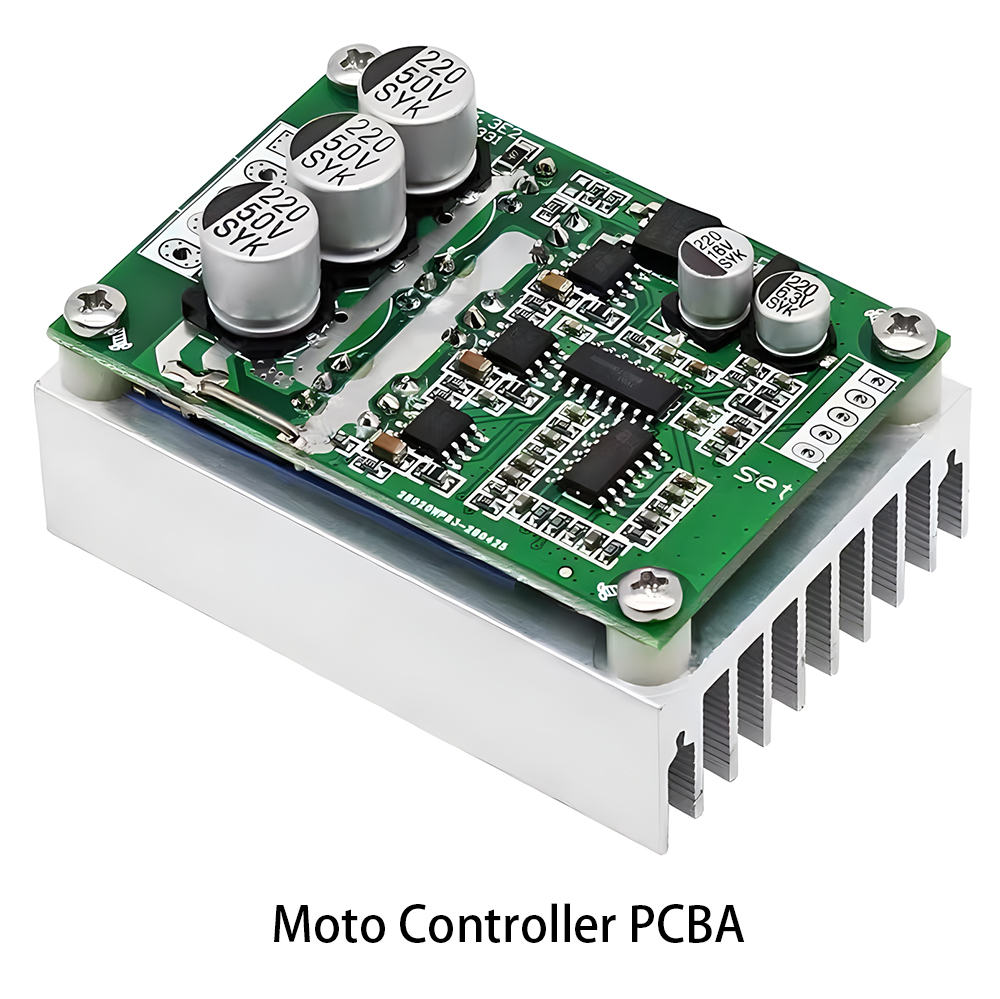 Industrial Control PCBA
Industrial Control PCBA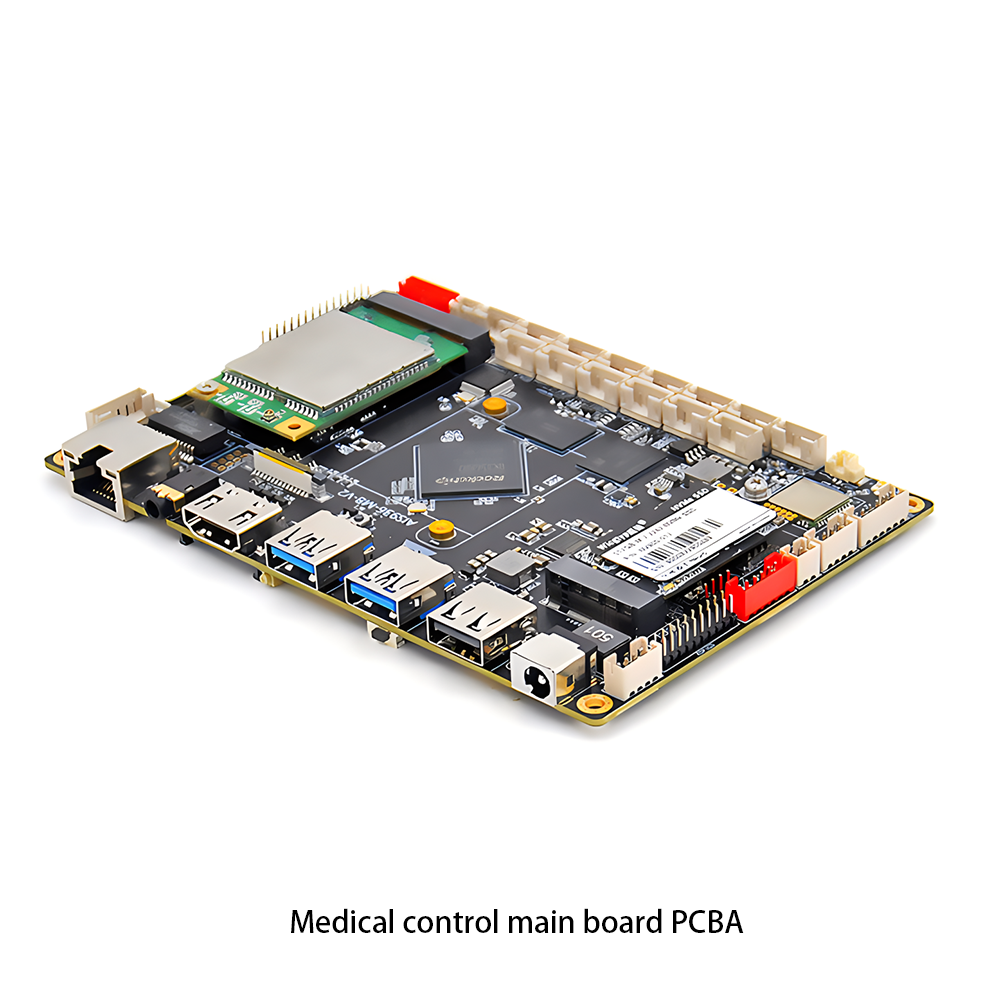 Medical Equipment PCBA
Medical Equipment PCBA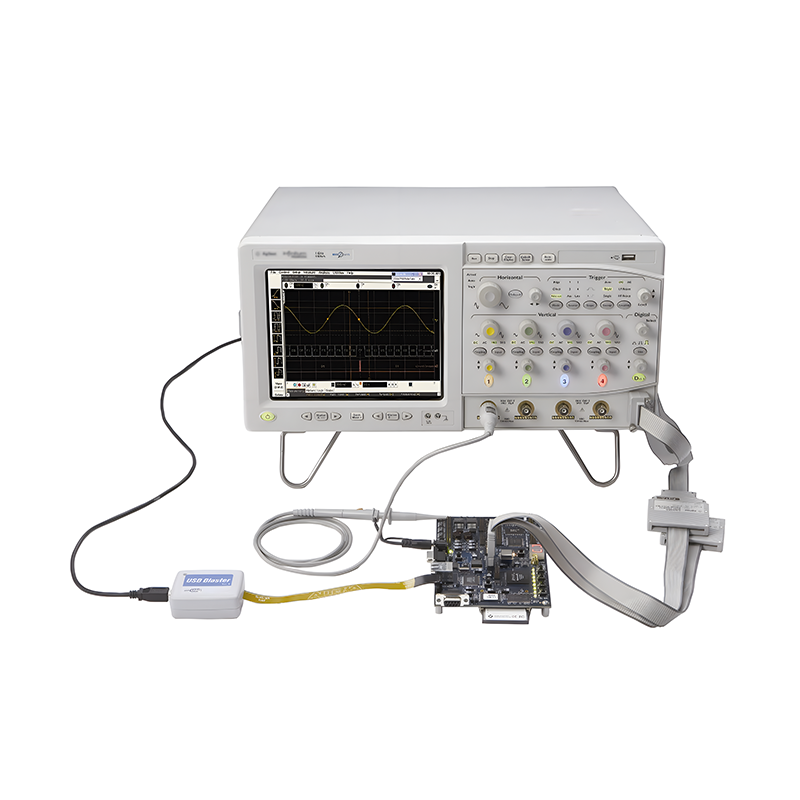 PCBA Testing Service
PCBA Testing Service Certification Application
Certification Application RoHS Certification Application
RoHS Certification Application REACH Certification Application
REACH Certification Application CE Certification Application
CE Certification Application FCC Certification Application
FCC Certification Application CQC Certification Application
CQC Certification Application UL Certification Application
UL Certification Application Transformers
Transformers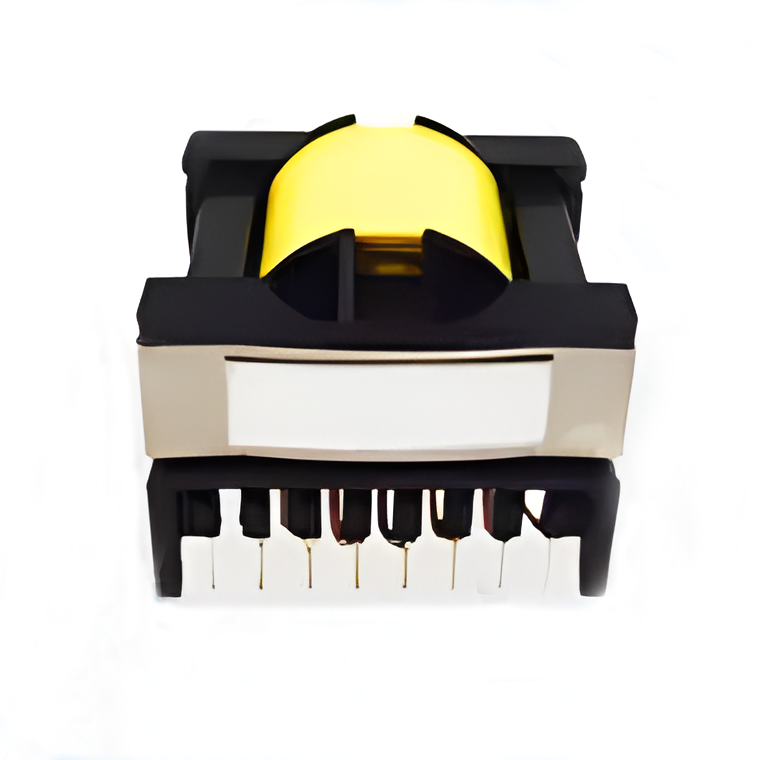 High Frequency Transformers
High Frequency Transformers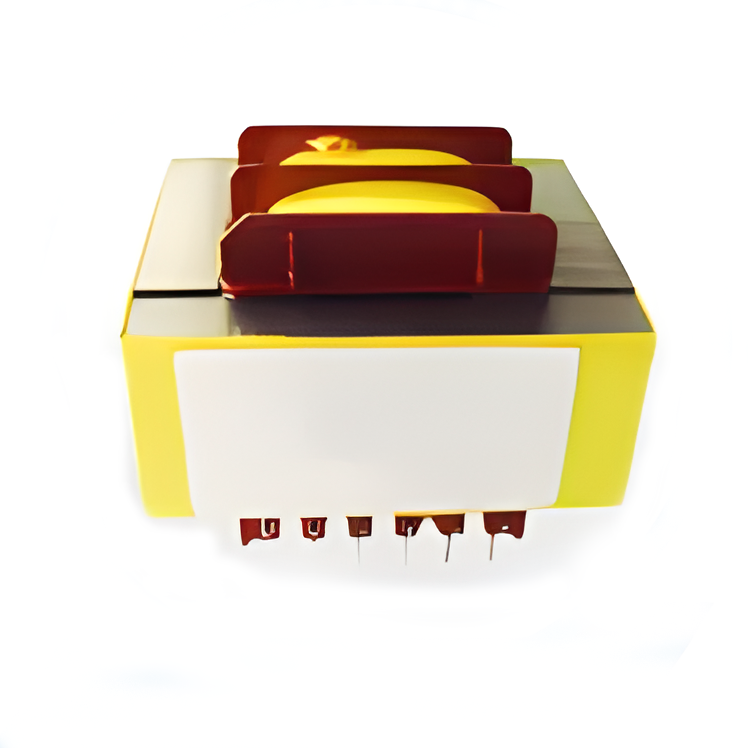 Low Frequency Transformers
Low Frequency Transformers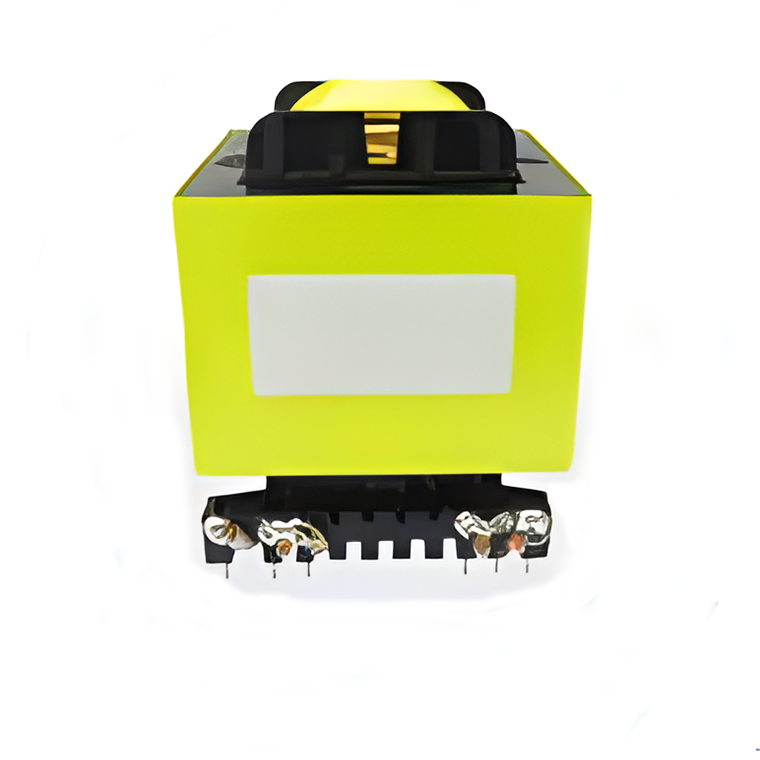 High Power Transformers
High Power Transformers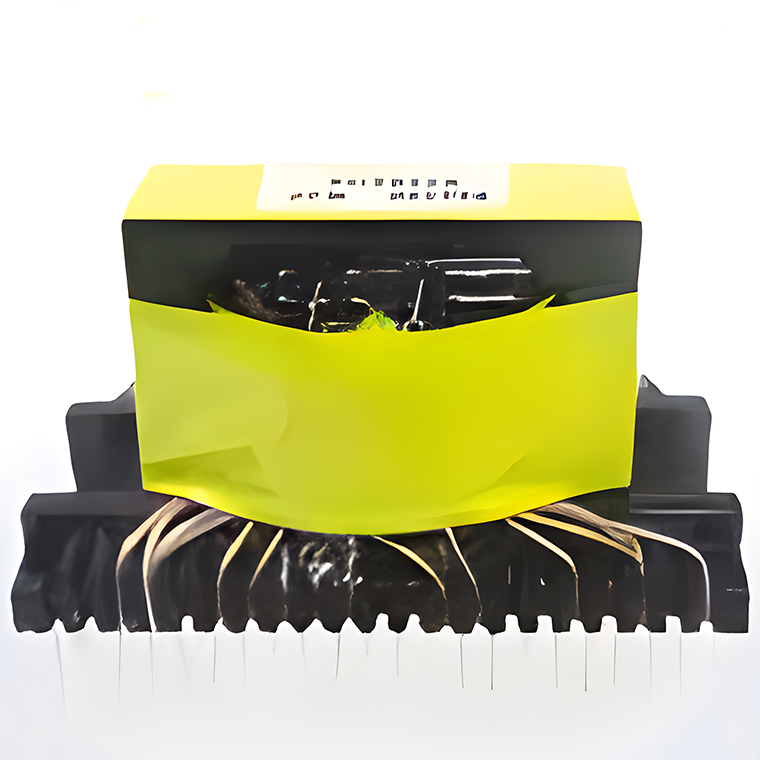 Conversion Transformers
Conversion Transformers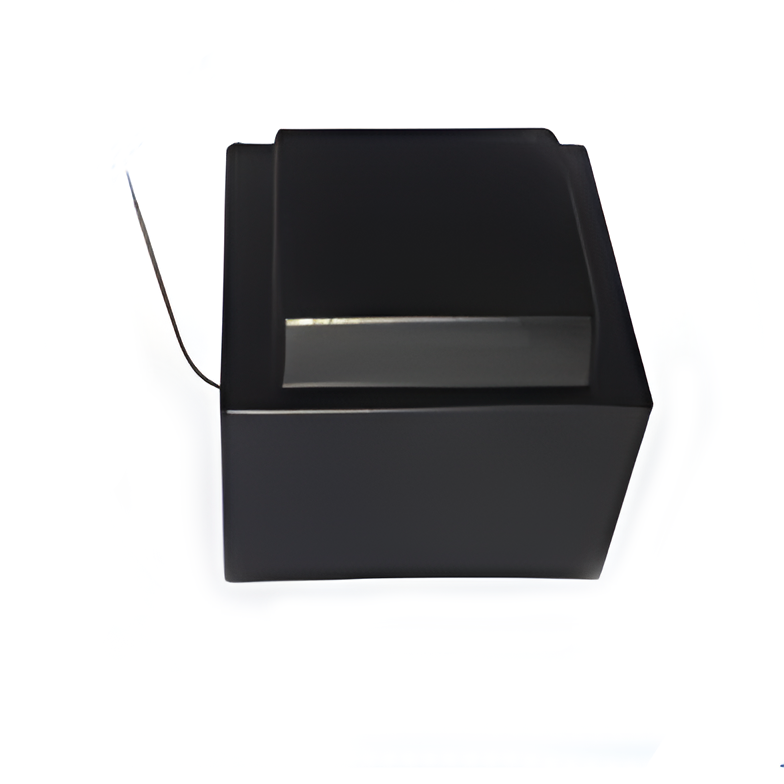 Sealed Transformers
Sealed Transformers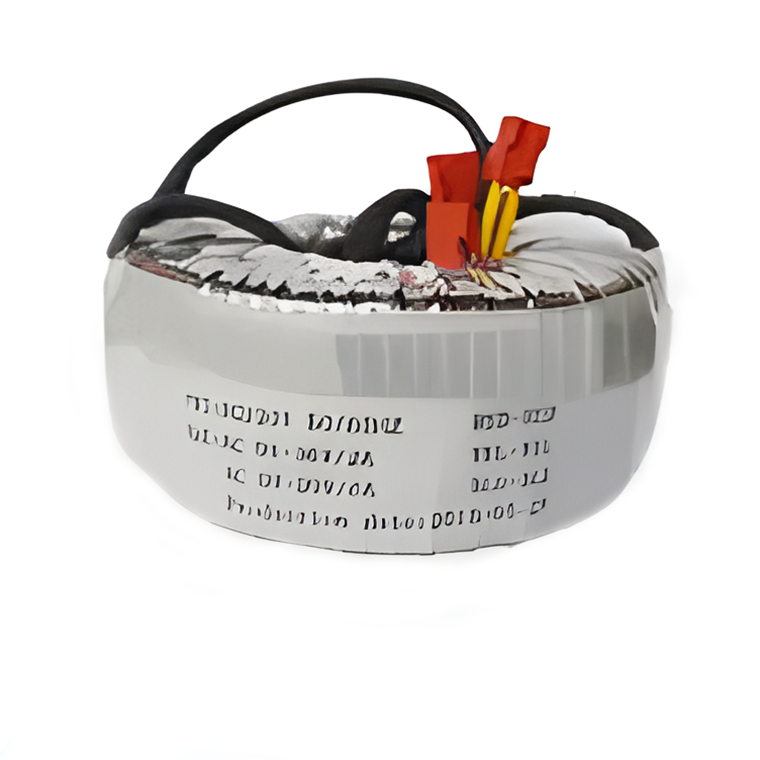 Ring Transformers
Ring Transformers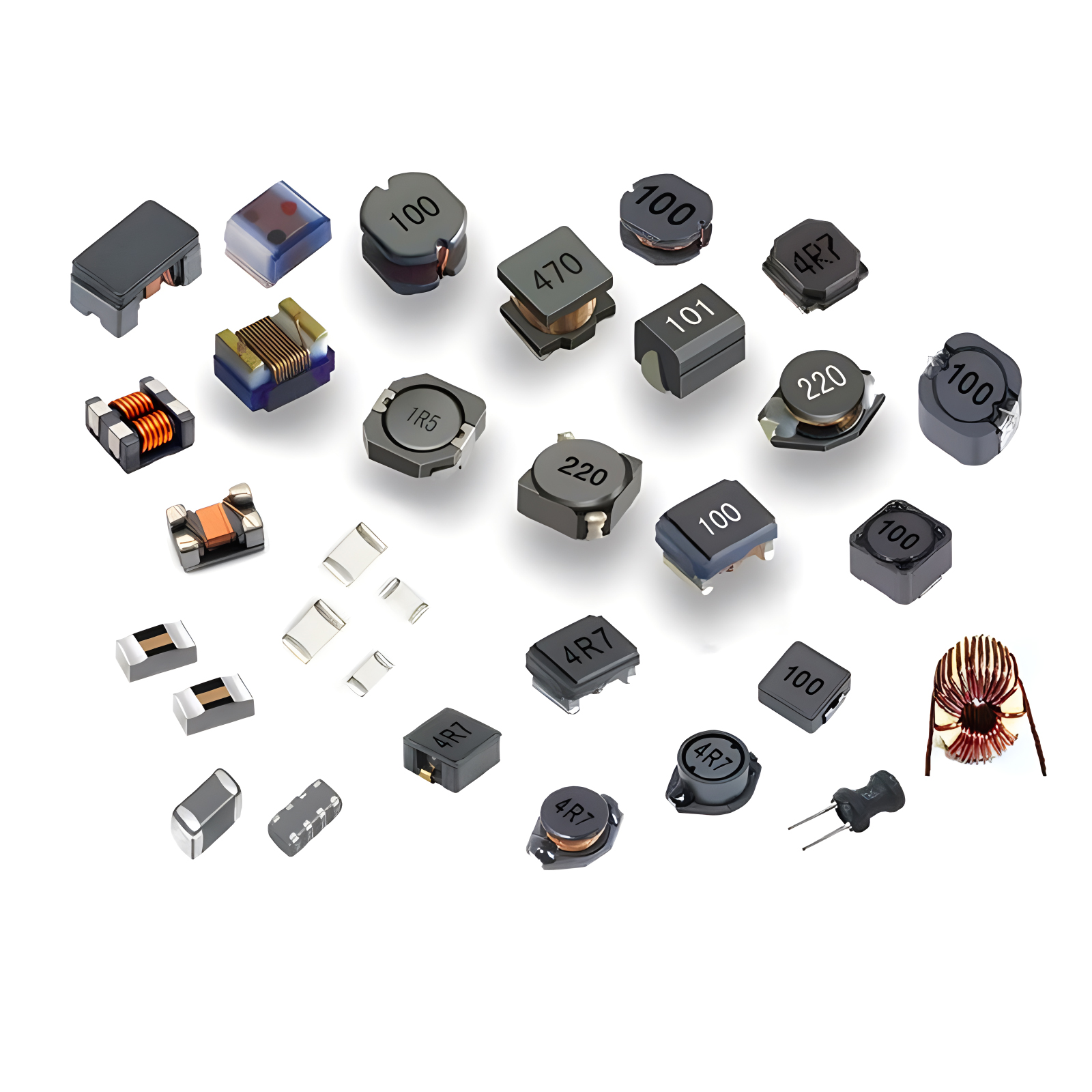 Inductors
Inductors Wires,Cables Customized
Wires,Cables Customized wires-cables
wires-cables Components sourcing
Components sourcing